Again less industrial waste

In 2005 the Dutch industry produced 18.8 million tonnes of industrial waste. This is 2 percent less than in 2004. It was the fourth year in a row in which Dutch industry produced less waste.
Most waste reused
The bulk of industrial waste is reused. In 2005 this was 16.7 million tonnes, of which 5 percent was used as fuel with recovering energy. The waste that is not reused is mainly incinerated (0.8 million tonnes) and dumped (0.9 million tonnes).
Industrial waste by industrial class
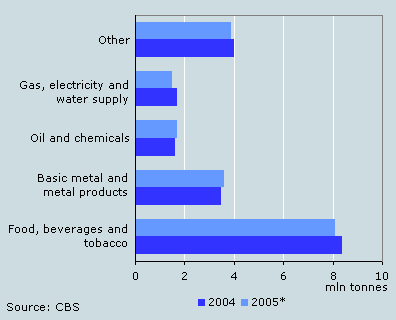
Greatest decrease in the food industry
The volume of industrial waste decreased mainly in the food and energy. The decrease mostly influenced the share of reuse in these size classes. In food, the volume of vegetable waste and dirt from beets decreased, mainly because of a lower waste production in the sugar industry.
In coal fired electricity plants, biomass is used more and more as a replacement fuel for coal. Biomass causes less ash as a waste product than coal when it is incinerated.
Industrial waste by category, 2005*

Most industrial waste from food
The food industry is still the biggest producer of waste, despite the decrease compared to 2004. Most vegetable and animal waste is reused, often in feed. Furthermore it is increasingly used as replacement fuel in electricity plants and cement ovens.
Reuse of industrial waste, 2005*

Reuse at a high level
Nearly all industrial classes reuse 85 percent or more of the waste. Energy companies have the highest level with 97 percent of reuse. Stone-like waste materials from coal-fired electricity plants such as slag, fly ashes and jarosite are often used in road construction and in the cement and plaster industries. Slag from the base metal industry is mostly used in the cement industry and in road construction.
René Jolly